PayPal NFT Marketplace
PayPal, the renowned international payment system, has recently made significant waves in the world of blockchain and digital assets. The company’s patent filings and applications for an NFT marketplace have captured the attention of industry experts and enthusiasts alike. With its sights set on the booming NFT space, PayPal is reinforcing its Web3 ambitions and aiming to revolutionize the way NFTs are traded, purchased, and transferred. This article will explore the details and implications of PayPal’s groundbreaking patent filing and its potential impact on the NFT ecosystem.
It’s day one as @PayPal's President and CEO. I'm fired up to join this team on a powerful mission and with a remarkable history of revolutionizing how millions around the world take control of their financial lives. PayPal team, let’s go change the world! 🚀 pic.twitter.com/PIZuY8iKn2
— Alex Chriss (@acce) September 27, 2023
PayPal NFT Marketplace Patent: A Game-Changing Solution
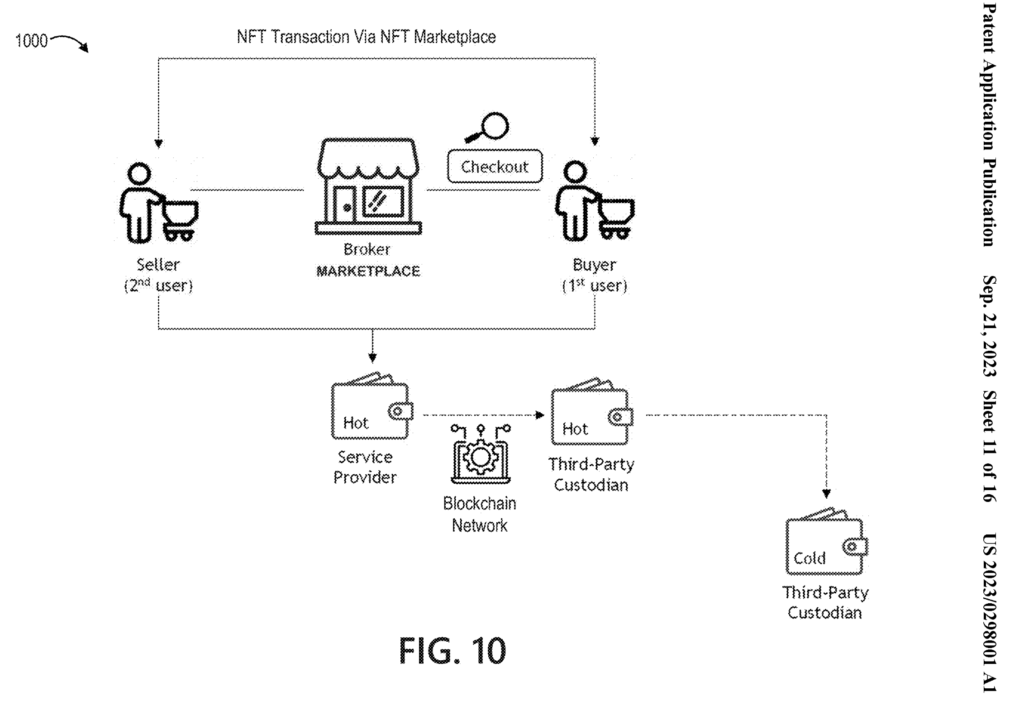
One of the key sources of information on PayPal’s NFT marketplace patent filing is an article published on CoinTelegraph. The patent application, filed six months ago and recently made public, outlines a unique method for executing NFT transactions both on and off-chain, accommodating multiple currencies. This innovative approach sets PayPal’s marketplace apart from existing exchanges and platforms, offering users a seamless and flexible experience for buying and selling NFTs.
Advancing NFT Transactions with Royalty-Friendly Features
Another source, NFT Now, sheds light on the exciting features that PayPal’s NFT marketplace aims to offer. The platform will allow users to leverage a third-party service provider for NFT transactions while unlocking the full potential of virtual assets through governance tokens. Additionally, the marketplace will support a wide range of digital data, including images, music, videos, art, collectibles, event tickets, legal documents, and physical rewards. Notably, the platform incorporates royalty provisions in its smart contracts, ensuring ongoing income for rights holders and creators.
Emphasizing Sustainability and Inclusivity
PayPal’s patent filing demonstrates the company’s commitment to creating a more sustainable and inclusive NFT ecosystem. By leveraging decentralized autonomous organizations (DAOs) and royalty mechanisms, the marketplace aims to foster equity and sustainability within its platform. Furthermore, the platform offers users the option to conduct off-chain transactions through an ‘omnibus wallet,’ reducing fees associated with blockchain network transactions. PayPal’s approach aligns with the growing demand for environmentally friendly and user-friendly NFT platforms.
A Strategic Move to Expand Web3 Strategy
The patent filing by PayPal is part of the company’s broader strategy to expand its presence in the Web3 space. As highlighted in an article on NFT Plazas, PayPal has been taking significant strides towards establishing its blockchain ecosystem. The introduction of its stablecoin, PYUSD, and the pursuit of an NFT marketplace patent demonstrate PayPal’s determination to leverage the potential of blockchain technology and tap into the growing popularity of NFTs.
Implications for the NFT Industry and Beyond
PayPal’s entry into the NFT marketplace arena has the potential to reshape the industry and drive mainstream adoption. As reported by NFT Gators, the company’s patent filing showcases its ambition to create a thriving marketplace where investors, creators, and users can freely engage in both on-chain and off-chain activities. By combining its extensive user base, trusted brand reputation, and innovative NFT trading features, PayPal has the opportunity to attract a wider audience to the world of digital collectibles and virtual assets.
Conclusion:
PayPal’s recent patent filings and applications for an NFT marketplace indicate a significant step forward for the adoption and integration of NFTs into the mainstream. By introducing a unique approach to NFT transactions, incorporating royalty provisions, and emphasizing sustainability and inclusivity, PayPal is poised to make a substantial impact on the NFT ecosystem. As the company continues to reinforce its Web3 ambitions, it is likely to play a pivotal role in shaping the future of NFT marketplaces and driving the wider adoption of blockchain technology.
Off-Chain Transactions
Off-chain transactions refer to transactions that occur outside of the blockchain network. In the context of NFT marketplaces, off-chain transactions provide an alternative method for buying, selling, and transferring NFTs without directly interacting with the underlying blockchain.
Off-chain transactions offer several advantages, including improved scalability, reduced transaction fees, and faster processing times. By moving transactions off-chain, platforms can alleviate the burden on the blockchain network, allowing for a smoother user experience and accommodating a higher volume of transactions.
One common approach to off-chain transactions is the use of layer-two solutions or sidechains. These are secondary protocols or blockchains that operate alongside the main blockchain and handle a significant portion of the transaction load. Layer-two solutions can process transactions more quickly and at a lower cost compared to the main blockchain, making them suitable for high-frequency and low-value transactions.
Another method for off-chain transactions is through the use of payment channels. Payment channels enable users to conduct multiple transactions off-chain, only settling the final result on the blockchain. This approach reduces the number of transactions recorded on the blockchain, resulting in cost savings and faster transaction times.
Off-chain transactions can be facilitated through various mechanisms, including centralized exchanges, custodial wallets, or third-party service providers. These intermediaries hold users’ NFTs and facilitate transactions on their behalf, offering a more user-friendly experience by abstracting the complexities of blockchain technology.
However, it’s important to note that off-chain transactions involve a certain level of trust in the intermediaries. Users must rely on these entities to securely hold and transfer their NFTs. Additionally, off-chain transactions may not provide the same level of transparency and immutability as on-chain transactions since the details of the transactions are not immediately recorded on the blockchain.
NFT Marketplace
An NFT marketplace is a digital platform where users can buy, sell, and trade non-fungible tokens (NFTs). NFTs are unique digital assets that represent ownership or proof of authenticity of a specific item or piece of content, such as artwork, collectibles, virtual real estate, music, videos, and more. NFTs have gained significant popularity in recent years, attracting artists, creators, collectors, and investors from various industries.
NFT marketplaces serve as the primary venue for the exchange of these digital assets. They provide a user-friendly interface that allows individuals to browse and discover a wide range of NFTs listed for sale. Users can search for specific categories, artists, or types of content to find NFTs that align with their interests.
When it comes to the transaction process, NFT marketplaces typically facilitate the buying and selling of NFTs through a secure and transparent mechanism. Sellers can list their NFTs for sale, set a price, and provide relevant details and metadata about the item. Buyers can then browse the available NFTs, place bids or purchase them directly using the marketplace’s native currency or supported cryptocurrencies.
One of the key features of NFT marketplaces is the integration of blockchain technology. NFTs are typically built on blockchain networks like Ethereum, Binance Smart Chain, or others. The blockchain ensures the uniqueness, provenance, and immutability of the NFTs, creating a transparent and tamper-proof record of ownership and transaction history.
NFT marketplaces also play a vital role in providing a platform for artists and creators to showcase and monetize their work. Artists can mint and list their NFTs for sale, allowing them to earn royalties on secondary sales. This provides artists with new revenue streams and greater control over their intellectual property.
Additionally, NFT marketplaces often feature community engagement and social features, enabling users to connect with creators, join discussions, and participate in events or auctions. Some marketplaces even offer additional services like fractional ownership, lending, or staking of NFTs, expanding the utility and potential investment opportunities associated with these digital assets.
As the popularity of NFTs continues to grow, so does the number of NFT marketplaces. Each marketplace may have its own unique features, user base, and supported blockchain networks or cryptocurrencies. It’s essential for users to research and choose reputable and secure marketplaces that align with their specific interests and requirements.